Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It is defined as a joint disease that touches hands, hips, knees, neck and lower back and it can cause pain and even disability when it is severe.
OSTEOPOROSIS
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS WITH ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD THERAPY
Electromagnetic therapy is a treatment that, in principle, makes use of electro-charged magnets to help improve your overall health and certain conditions.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (magnetic field) is the latest suggested treatment for various musculoskeletal conditions. The use of pulsed electromagnetic frequencies helps body cells stimulate a proper proportion of potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium. Having such a ratio balanced the therapy helps reduce pain, improves bone metabolism, and accelerates the bone regeneration process which is vital for a patient diagnosed with osteoporosis. It immerses a magnetic field in patients’ bodies through the use of magnets on big machine devices. Its rare side effects are generally nausea and feeling dizzy.
The therapy is described as totally painless by patients. It lasts roughly 50 minutes and the patient has to only lay down on a cloth for the therapy to be applied. Electromagnetic therapy is used in conjunction with conventional medical treatment and there are no impactful complications a patient can experience.
In pulsed electromagnetic field therapy , the magnets are electro-charged but they are not harmful to your body because the intensity and duration are properly registered and tested to provide the expected results.
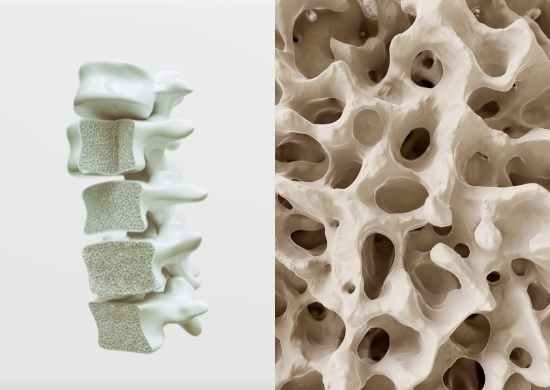
WHAT IS OSTEOPOROSIS?
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass production. The former leads to the fragility of bones and therefore raises the risks of experiencing fractures. Keeping our bone tissues strong, our body needs to regenerate them, replacing the loss of old bones with the formation of new ones. The regeneration process becomes more difficult to happen in the late stages of our lives because of low levels of estrogen in women and testosterone in men. Therefore, there is a need for a way that helps repair bone tissues and contributes to their regeneration process so that it can strengthen our bone metabolism and help people suffering from osteoporosis have an easier life and carry out normal daily activities. The latest advancements in medicine suggest alternatives to treating it by creating an electromagnetic field around the patient’s body.
OSTEOPOROSIS SYMPTOMS
Osteoporosis has no visible symptoms. Only if a bone is broken without intentionally causing its break, can one tell that there is some type of health problem a person is experiencing. People should be aware of sudden bone fractures because these are connected to osteoporosis. A patient can understand whether their bone-breaking is osteoporosis or not by consulting a physiotherapist. However, there are some health problems one can relate to osteoporosis before seeing a doctor. For example, osteoporosis in the vertebral area is manifested in the form of sudden back pain, radicular pain (pain in one’s back as if they are being shot), and spinal cord compression. There are other skeletal areas in our body that can be broken such as the shoulders, hips, and wrists. Sudden fractures in such areas are to be considered seriously.
The most notable form of osteoporosis is the skeletal damage that is caused by vertebral fractures and then they result in stooped and bad posture therefore seemingly loss of height. A patient also feels chronic pain and such pain impairs a patient’s mobility.
WHAT CAUSES OSTEOPOROSIS?
Most of the diseases or health conditions people suffer from have two main sources people receive or develop from: unchangeable and changeable risk factors.
UNCHANGEABLE CAUSES
Factors one cannot change as in the case of age, gender, ethnicity, and/or family history. However, there are also some other factors one can avoid based on their lifestyle. Such factors include alcohol, smoking, eating, malnutrition, and physical activity.
The most important risk contributor to osteoporosis is age. The older we get the higher chances we have to suffer from osteoporosis. There is a peak age of bone formation and that is generally 25 to 30. After this age, the new bones’ formation does not overcome the loss of the old ones. Such a ratio weakens our bones and results in health conditions such as osteoporosis. In medicine, such type of osteoporosis is known as senile osteoporosis.
The second type of osteoporosis is postmenstrual, which is caused due to relatively low estrogen in women and a decrease in testosterone in men. As for women, such decrease comes from menopause or any possible removal of ovaries and it is for both genders associated with a speedy reduction in mineral density. The reduction of bones’ mineral density weakens them and raises the likelihood of experiencing osteoporosis. There was noted a higher tendency for women to experience osteoporosis than men due to the above-mentioned reasons.
Interestingly, it is suggested that osteoporosis tends to occur mostly in Asian and European ancestors. However, osteoporosis is not an exclusive health condition to such ethnicities. It can occur in all ethnic communities.
Genetics is definitely a risk factor regarding the chances of experiencing and suffering osteoporosis. Having family members that have suffered osteoporosis, the chances are higher for the ascendants to experience it too. In the same way, people who have had a fracture are more likely to experience another fracture or osteoporosis than the ones who have not.
CHANGEABLE RISC FACTORS
Alcohol intake can be beneficial regarding bone density, yet heavy drinking can increase the risk of bone fractures. Heavy drinking refers to an above-normal intake of alcohol (3 units per day).
The importance of Vitamin D is strongly connected with bones’ strength and therefore a contributor to bone metabolism. Thus, low levels of vitamin D are indirectly related to decreased bone mineral density. Vitamin D insufficiency, which is quite common among elderly people, is associated with increasing levels of Parathyroid Hormone production. PTH increases bone weakening and the latter results in bone loss.
Another factor that might contribute to osteoporosis, despite not directly, is tobacco smoking. It is proposed that smoking inhibits osteoblasts’ activity which is a cause of osteoporosis. Smoking is associated with increased estrogen breakdown, loss of weight and sometimes contributes to earlier menopause. All the mentioned consequences of smoking contribute to the decreased mineral density of bones. Weak bones mean higher chances of fractures and sudden fractures are related to osteoporosis.
Nutrition is the most important contributor to a healthy life. The opposite of it: malnutrition results in numerous developed health conditions, diseases, and illnesses. In the case of osteoporosis, foods that are rich in calcium, zinc, magnesium, iron, copper, boron, fluoride, and vitamins A, E, D, K are important to bone mass production and strong bone density. It is suggested that a diet rich in proteins helps with lower spine density but does not show significant improvement with other bones. There is some link between protein intake and blood acidity. The lower the level of protein intake, the higher the blood acidity is. The latter is a risk factor for bones. Also, the intake of omega 6, omega 3, and other related fats can contribute to osteoporosis. Soft drinks are believed to increase the risk of osteoporosis due to the phosphoric acid it contains.
There are two main processes: bones go through bone formation (when the old ones are replaced by new ones) and bone remodeling (when activity strengthens the bones and muscles).
Thus, inactivity and being underweight can result in bone loss which increases the chances of occurrence of osteoporosis. It is believed that the incidence of osteoporosis is lower in people who are overweight. It is also worth noting that excessive endurance physical activity may lead to decreased bone density and as a result higher chances of osteoporosis. Intense training might be a higher risk for females than male athletes. The reason lies in the effects of training on menstruation and the production of amenorrhea (the absence of menstruation).
Health starts with knowing!
OSTEOPOROSIS TREATMENT
One should address any above-noted pain related to osteoporosis to a physiotherapist or wellness professional. It usually examines the proportion of mineral bones in the patient’s problematic area(s) through a density test. According to the test’s results and the severity of osteoporosis in a patient’s bones, a doctor suggests medications or treatments.
Osteoporosis medications are expected to reduce the rate at which a patient’s bones break. There are some medications that can speed up the process of new bone-building and some others can strengthen the bones and reduce the risks of fractures.
When the estimated risk of bone-breaking is diagnosed as not high, the treatment may not include medication at all. However, your physiotherapist will suggest you work on reducing risk factors (modifiable ones; such as alcohol, smoking, inactivity, nutrition) to decrease bone loss and prevent falls.
When the estimated risk of fracture is diagnosed as high, medication is prescribed. Generally, bisphosphonates’ examples are prescribed. They are alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate, and zoledronic. The medicine should be taken properly to lower the chances of side effects. A patient must be aware that such medications may be followed by heart bum, nausea, abdominal pain, headache, muscle aches, and sometimes fever. Less likely side effects are breaking of thighbones or later than expected healing of a jawbone in case of any dental surgery.
Denosumab is also prescribed to produce bone density and reduce fractures. The less likely side effects are similar to bisphosphonates. This type of medication continues the whole life and it is taken every six months.
Doctors may suggest hormone therapy to osteoporosis patients. This therapy improves health bones by improving low symptoms of estrogen in women and testosterone in men.
When the patient is diagnosed with severe osteoporosis these types of medications are suggested:
Teriparatide is a drug that stimulates new bone growth. It is taken as an injection every day for two years. A similar medication is abolopantide. Romosozumab is also an injection that helps bone building. It is taken every month for a year. A patient may need another drug after the treatment with one of the above medications.
Read about conditions that EMT treats
Disc Conditions
Human body’s vertebrae are separated by discs which can be flat, round or fibrous. One experiences disc conditions when damaged discs start moving out of the alignment or even break down.
Sports Injuries
Sports injuries occur when somebody engages in strenuous or improper physical activity. Lack of warm up exercises before training increases the risks of experiencing sports injuries.
Wound Healing
Wound healing is a dynamic and complex process that consists of four continuous stages such as: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling.
Wellness and Fitness
Wellness and health are commonly used interchangeably but they have a significant difference in meaning. Our health or lack of it is a composition of diagnosis of any diseases, family history and predisposition to certain diseases and injuries.
Veterinary Services
Animal wellness refers to the general health of our pets. An animal is subject to almost the same health problems as a human and needs to be treated by veterinarians in veterinary centers.